In today’s globally connected trade ecosystem, ensuring your supply chain is secure is no longer optional—it’s expected. Businesses that export to the United States or work with U.S.-based importers must prioritize supply chain security, and that’s where the CTPAT compliance checklist comes in.
his blog breaks down the key compliance areas your business must address to meet the Customs Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (CTPAT) standards and stay ahead in international trade.
What Is the CTPAT Compliance Checklist ?
The CTPAT compliance checklist is a structured framework issued by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). It contains 13 mandatory criteria that businesses must meet to demonstrate their supply chain is protected against threats such as terrorism, theft, smuggling, and forced labor.
This checklist applies to manufacturers and exporters to understand CTPAT Minimum Security Criteria for Foreign Manufacturers:
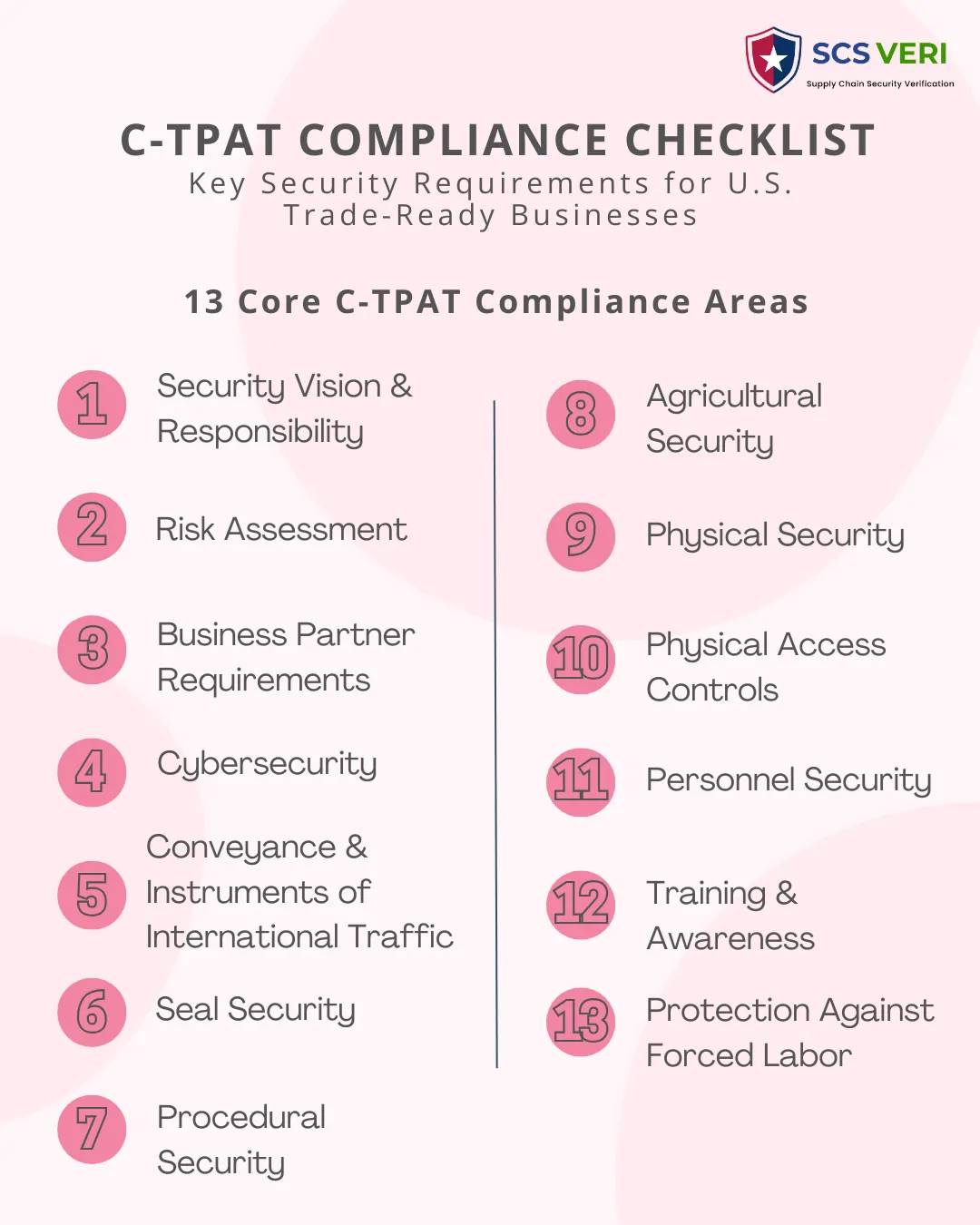
13 Key Areas of the CTPAT Compliance Checklist
Here are the core security requirements every business must comply with under the CTPAT program:
1. Security Vision and Responsibility
Establish a written policy and assign a dedicated individual or team responsible for overseeing supply chain security.
2. Risk Assessment
Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities within your facility and also in supply chain—from suppliers to transportation and logistics.
3. Business Partner Requirements
Ensure that your facility, vendors and service providers meet minimum security standards through screening, validation, and contracts.
4. Cybersecurity
Implement security measures to safeguard trade-related data and prevent cyberattacks, unauthorized access, or data leaks.
5. Conveyance and Instruments of International Traffic (IIT)
Secure trucks, containers, and other vehicles used for shipping with measures like inspection procedures and secure parking areas.
6. Seal Security
Use high-security seals on containers and monitor their application, control, and removal throughout the shipping process.
7. Procedural Security
Document and enforce SOPs for cargo handling, documentation, shipping, and receiving to prevent loss or tampering.
8. Agricultural Security
Take steps to prevent pest contamination and ensure compliance with agricultural import regulations.
9. Physical Security
Implement physical barriers such as fencing, surveillance systems, locks, and alarms at production and storage facilities.
10. Physical Access Controls
Restrict access to sensitive areas through ID checks, visitor logs, security guards, and access card systems.
11. Personnel Security
Verify employee identity and conduct background checks before hiring. Enforce policies for reporting suspicious behavior.
12. Education, Training, and Awareness
Train all relevant employees, vendors and service providers in CTPAT requirements, internal protocols, and how to report potential threats or breaches.
13. Protection Against Forced Labor
Ensure that your supply chain is free from child labor, forced labor, or unethical labor practices. Maintain transparency and documentation to prove compliance.
Why This Checklist Matters ?
Adhering to the CTPAT checklist ensures your business:
Pro Tip: Self-Audit Before the CBP Does
Get ready to conduct a self-assessment using this checklist. Identify any gaps and act on them proactively to demonstrate readiness during your next CTPAT validation or third-party audit.
How RSJ Inspection Can Help
RSJ Inspection offers independent CTPAT audit/assessment services to help you assess how well your operations meet CTPAT standards. Our experienced auditors work with:
- Exporters and suppliers shipping to the U.S.
- Factories, warehouses, and distribution centers
We provide objective reports outlining compliance status and next steps to ensure your supply chain is aligned with CBP expectations.
Ready to Secure Your Supply Chain?
Let RSJ Inspection through audit/assessment help you to assess your CTPAT compliance status to enable you to make corrections (if needed), so as to strengthen your security practices for readiness for U.S. trade.



